Get started with the TypeScript SDK
Learn how to set up the TypeScript SDK and how to use example code.
This step-by-step guide leads you through setting up and making API calls using the TypeScript SDK.
Objectives of the get started guide
By the end of this guide you will have:
Requirements
A Project with a configured API Client.
The following (or later) must be installed before the TypeScript SDK can be used:
- Node v12.22.7
- npm v6 OR yarn v1.22.17
Placeholder values
Example code in this getting started guide uses placeholders that should be replaced with the following values:
| Placeholder | Replace with | From |
|---|---|---|
{projectKey} | project_key | your API Client |
{clientID} | client_id | your API Client |
{clientSecret} | secret | your API Client |
{scope} | scope | your API Client |
{region} | your locale | Hosts |
Install the TypeScript SDK
Use the following commands to install SDK components from npm or Yarn.
| SDK | npm | Yarn |
|---|---|---|
| SDK Client | npm install @commercetools/sdk-client-v2 | yarn add @commercetools/sdk-client-v2 |
| HTTP API | npm install @commercetools/platform-sdk | yarn add @commercetools/platform-sdk |
| Import API | npm install @commercetools/importapi-sdk | yarn add @commercetools/importapi-sdk |
| Machine Learning API | npm install @commercetools/ml-sdk | yarn add @commercetools/ml-sdk |
| Audit Log API | npm install @commercetools/history-sdk | yarn add @commercetools/history-sdk |
The SDK Client and the HTTP API must be installed. The Import API, Machine Learning API, and Audit Log API are only needed for more specific use cases.
Create a ClientBuilder file
Create a new file called BuildClient.ts and insert the following code.
This code creates a Client that is used to make API calls.
import fetch from 'node-fetch';import {ClientBuilder,// Import middlewarestype AuthMiddlewareOptions, // Required for authtype HttpMiddlewareOptions, // Required for sending HTTP requests} from '@commercetools/sdk-client-v2';const projectKey = '{projectKey}';const scopes = ['{scope}'];// Configure authMiddlewareOptionsconst authMiddlewareOptions: AuthMiddlewareOptions = {host: 'https://auth.{region}.commercetools.com',projectKey: projectKey,credentials: {clientId: '{clientID}',clientSecret: '{clientSecret}',},scopes,fetch,};// Configure httpMiddlewareOptionsconst httpMiddlewareOptions: HttpMiddlewareOptions = {host: 'https://api.{region}.commercetools.com',fetch,};// Export the ClientBuilderexport const ctpClient = new ClientBuilder().withProjectKey(projectKey) // .withProjectKey() is not required if the projectKey is included in authMiddlewareOptions.withClientCredentialsFlow(authMiddlewareOptions).withHttpMiddleware(httpMiddlewareOptions).withLoggerMiddleware() // Include middleware for logging.build();
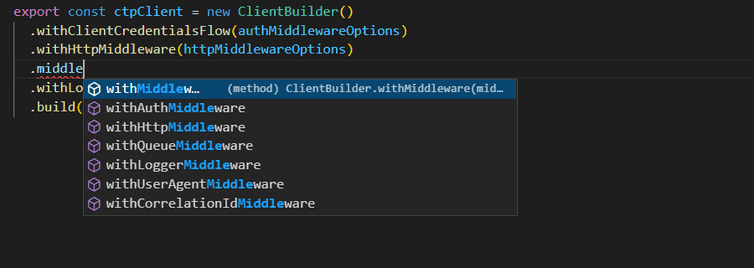
Adding middleware
Using this example code configures authMiddlewareOptions and httpMiddlewareOptions to handle auth and HTTP requests respectively. You can configure and use other middleware based on your requirements and add them to ctpClient with method chaining:
Create the Client
Create a new file and include the following code:
import { ctpClient } from './BuildClient';import {ApiRoot,createApiBuilderFromCtpClient,} from '@commercetools/platform-sdk';// Create apiRoot from the imported ClientBuilder and include your Project keyconst apiRoot = createApiBuilderFromCtpClient(ctpClient).withProjectKey({ projectKey: '{projectKey}' });// Example call to return Project information// This code has the same effect as sending a GET request to the commercetools Composable Commerce API without any endpoints.const getProject = () => {return apiRoot.get().execute();};// Retrieve Project information and output the result to the loggetProject().then(console.log).catch(console.error);
apiRoot can now be used to build requests to the Composable Commerce API.
This code includes getProject() as an example. If you run this code, the Project is returned.
How to structure your API call
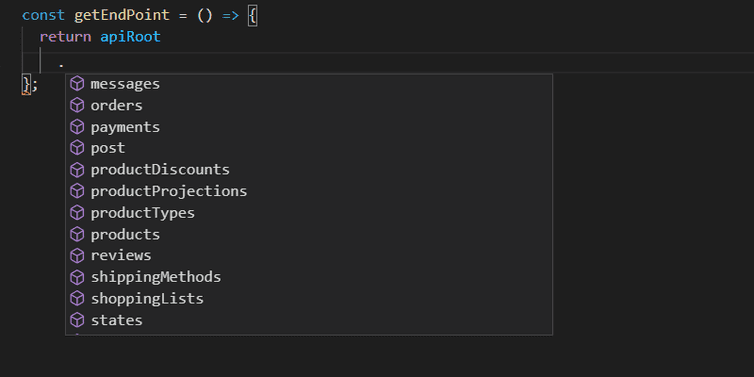
Add an endpoint
An endpoint should be added to apiRoot. The following targets the Customers endpoint:
apiRoot.customers();
If your IDE supports auto-complete, the full list of endpoints can be viewed.
If no endpoint is specified, the Project is referenced.
Query a specific entity using withID() or withKey()
To query a specific entity (such as an individual Customer), include its id or key.
apiRoot.customers().withId({ ID: 'a-customer-id' });
apiRoot.customers().withKey({ key: 'a-customer-key' });
This allows you to target GET or POST requests to specific entities.
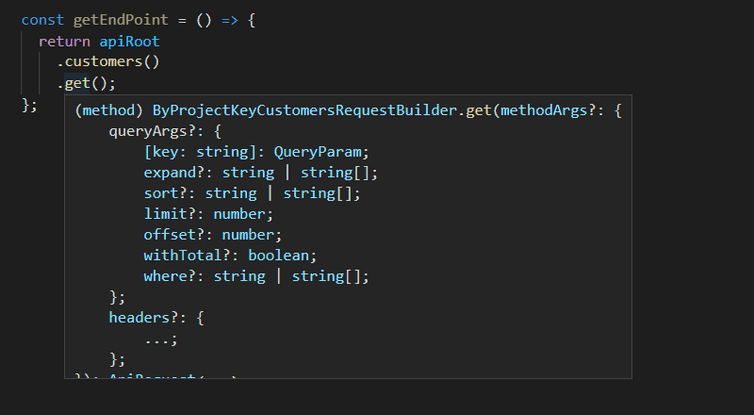
Add the method
After selecting the endpoint, select a method to use. get() is used to query entities. post() is used to create and update entities.
apiRoot.customers().withId({ ID: 'a-customer-id' }).get();
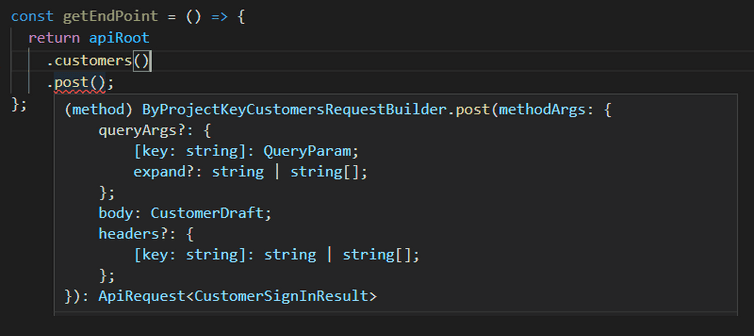
Adding parameters and payloads
Parameters for querying entities can be included within get(). Parameters and payloads for updating and creating entities should be included within post().
When getting the Customer endpoint, optional parameters can be included to modify what Customers are returned:
When posting to the Customer endpoint, a body payload must be included. This payload (CustomerDraft) creates a new Customer:
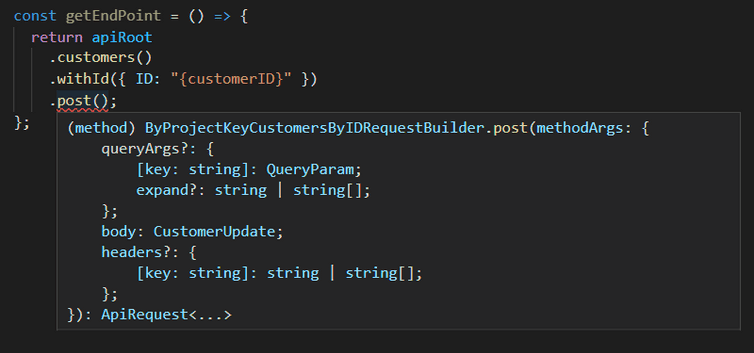
When posting to a specific Customer, a body payload must be included. This payload (CustomerUpdate) updates the specified Customer:
.execute() .then() .catch()
.execute() sends the API request.
.then() adds functionality that should follow the API request. In the following example code, then() is used to output the response to the console.
.catch() should be included for assisting with debugging and error handling.
apiRoot.customers().withId({ ID: 'a-customer-id' }).get().execute().then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
Try our example code
The following example code covers some basic operations and is intended to provide you with an insight into how to create, query, and modify entities within commercetools Composable Commerce.
This code can be easily adapted and built upon to help you learn how to use the TypeScript SDK to interact with your Project.
Manage Customers
Create a Customer
When creating Customers using the HTTP API, a CustomerDraft must be created and posted to the Customers endpoint.
The CustomerDraft has two required fields: email and password.
This example code creates a Customer with the TypeScript SDK and returns the new Customer resource:
const createCustomer = () => {return apiRoot.customers().post({body: {email: 'typescript-sdk@example.com',password: 'examplePassword',},}).execute();};// Create the customer and output the result to the log.createCustomer().then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
{"customer": {"id": "{customerID}","version": 1,"createdAt": "2022-01-21T18:32:25.573Z","lastModifiedAt": "2022-01-21T18:32:25.573Z","lastModifiedBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"createdBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"email": "typescript-sdk@example.com","password": "****aGg=","addresses": [],"shippingAddressIds": [],"billingAddressIds": [],"isEmailVerified": false,"stores": [],"authenticationMode": "Password"}}
Take note of the {customerID} in your response as it is used as a placeholder in following examples.
Query a Customer
Your new Customer can be queried by adding .withId({ID: {customerID}}) after the .customers() endpoint:
// Return a Customer based on their IDconst queryCustomer = (customerID: string) => {return apiRoot.customers().withId({ ID: customerID }).get().execute();};// Query the Customer and output the result to the log.queryCustomer('{customerID}').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
When this code is run, you retrieve all the data of the Customer.
If you query a Customer with an ID that does not exist, the API returns a 404 Not Found error.
Add a Customer name
The Composable Commerce API uses update actions to change existing entities.
When an array of update actions is posted to a Customer, the Customer is updated based on the specified update actions and their values.
The required update actions for changing a Customer name are Set First Name and Set Last Name.
The current version of the Customer is also required.
The version of a new Customer is 1. This value is incremented every time an update action is applied to the Customer.
If the specified version does not match the current version, the request returns an error.
This example code updates a Customer with the TypeScript SDK and returns the updated Customer resource:
const updateCustomerName = (customerID: string) => {return apiRoot.customers().withId({ ID: customerID }).post({body: {version: 1,actions: [{action: 'setFirstName',firstName: 'John',},{action: 'setLastName',lastName: 'Smith',},],},}).execute();};// Update the customer and output the result to the log.updateCustomerName('{customerID}').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
{"id": "{customerID}","version": 3,"createdAt": "2022-01-21T18:32:25.573Z","lastModifiedAt": "2022-01-21T18:34:54.644Z","lastModifiedBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"createdBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"email": "typescript-sdk@example.com","firstName": "John","lastName": "Smith","password": "****aGg=","addresses": [],"shippingAddressIds": [],"billingAddressIds": [],"isEmailVerified": false,"stores": [],"authenticationMode": "Password"}
Find a Customer by their email address
As the email of a Customer is unique, it is a dependable way to find a Customer.
Customers can be found by their email address by querying the Customers endpoint with a where parameter.
In the commercetools Composable Commerce API, where uses a Query Predicate.
This example code finds a Customer by their email address with the TypeScript SDK and returns the Customer resource:
const returnCustomerByEmail = (customerEmail: string) => {return apiRoot.customers().get({queryArgs: {where: `email="${customerEmail}"`,},}).execute();};returnCustomerByEmail('typescript-sdk@example.com').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
{"limit": 20,"offset": 0,"count": 1,"total": 1,"results": [{"id": "{customerID}","version": 3,"createdAt": "2022-01-21T18:32:25.573Z","lastModifiedAt": "2022-01-21T18:34:54.644Z","lastModifiedBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"createdBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"email": "typescript-sdk@example.com","firstName": "John","lastName": "Smith","password": "****aGg=","addresses": [],"shippingAddressIds": [],"billingAddressIds": [],"isEmailVerified": false,"stores": [],"authenticationMode": "Password"}]}
If there is no Customer with the specified email address, then an empty query result is returned:
{"limit": 20,"offset": 0,"count": 0,"total": 0,"results": []}
Manage Products
Creating Products requires more steps than creating Customers. This is due to how Products are modeled in commercetools.
Before a Product can be created, you must first create a ProductType.
Create a ProductType
When creating ProductTypes using the HTTP API, a ProductTypeDraft must be created and posted to the ProductTypes endpoint.
The ProductTypeDraft has two required fields: name and description.
This example code creates a ProductType with the TypeScript SDK and returns the new ProductType resource:
const createProductType = () => {return apiRoot.productTypes().post({body: {name: 'The name of your ProductType',description: 'The description of your ProductType',},}).execute();};// Create the ProductType and output the result to the logcreateProductType().then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
{"id": "{productTypeID}","version": 1,"createdAt": "2022-01-21T18:16:09.954Z","lastModifiedAt": "2022-01-21T18:16:09.954Z","lastModifiedBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"createdBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"name": "The name of your ProductType","description": "The description of your ProductType","classifier": "Complex","attributes": []}
Take note of the {productTypeID} in your response as it is used as a placeholder in following examples.
Create a Product
When creating Products using the HTTP API, a ProductDraft must be created and posted to the Products endpoint.
The ProductDraft has three required fields: name, productType, and slug.
This example code creates a Product with the TypeScript SDK and returns the new Product resource:
const createProduct = (productTypeID: string) => {return apiRoot.products().post({body: {name: {en: 'English name for your Product',de: 'German name for your Product',},productType: {typeId: 'product-type',id: productTypeID,},slug: {en: 'human-readable-url-for-english-product',de: 'human-readable-url-for-german-product',},},}).execute();};// Create the Product and output the result to the logcreateProduct('{productTypeID}').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
{"id": "{productID}","version": 1,"createdAt": "2022-01-21T18:18:26.331Z","lastModifiedAt": "2022-01-21T18:18:26.331Z","lastModifiedBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"createdBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"productType": {"typeId": "product-type","id": "{productTypeID}"},"masterData": {"current": {"name": {"en": "English name for your Product","de": "German name for your Product"},"categories": [],"categoryOrderHints": {},"slug": {"en": "human-readable-url-for-english-product","de": "human-readable-url-for-german-product"},"masterVariant": {"id": 1,"prices": [],"images": [],"attributes": [],"assets": []},"variants": [],"searchKeywords": {}},"staged": {"name": {"en": "English name for your Product","de": "German name for your Product"},"categories": [],"categoryOrderHints": {},"slug": {"en": "human-readable-url-for-english-product","de": "human-readable-url-for-german-product"},"masterVariant": {"id": 1,"prices": [],"images": [],"attributes": [],"assets": []},"variants": [],"searchKeywords": {}},"published": false,"hasStagedChanges": false},"lastVariantId": 1}
Take note of the {productID} in your response as it is used as a placeholder in following examples.
Query your Product
Your new Product can be queried by adding .withId({ID: {customerID}}) after the .products() endpoint:
// Return a Product based on its IDconst queryProduct = (productID: string) => {return apiRoot.products().withId({ ID: productID }).get().execute();};// Query the Product and output the result to the log.queryProduct('{productID}').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
When this code is run, you retrieve all the data of the Product.
If you query a Product with an ID that does not exist, the API returns a 404 Not Found error.
Add a Product key
Adding a key to a Product requires the Set Key update action.
The current version of the Product is also required.
The version of a new Product is 1. This value is incremented every time an update action is applied to the Product.
If the specified version does not match the current version, the request returns an error.
This example code adds a key to a Product with the TypeScript SDK and returns the updated Product resource:
const addKeyToProduct = (productID: string) => {return apiRoot.products().withId({ ID: productID }).post({body: {version: 1,actions: [{action: 'setKey',key: 'new-product-key', // If this key is blank or not included, the API removes any existing key},],},}).execute();};addKeyToProduct('{productID}').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
{"id": "{productID}","version": 2,"createdAt": "2022-01-21T18:18:26.331Z","lastModifiedAt": "2022-01-21T18:26:27.910Z","lastModifiedBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"createdBy": {"clientId": "{clientID}","isPlatformClient": false},"productType": {"typeId": "product-type","id": "{productTypeID}"},"masterData": {"current": {"name": {"en": "English name for your Product","de": "German name for your Product"},"categories": [],"categoryOrderHints": {},"slug": {"en": "human-readable-url-for-english-product","de": "human-readable-url-for-german-product"},"masterVariant": {"id": 1,"prices": [],"images": [],"attributes": [],"assets": []},"variants": [],"searchKeywords": {}},"staged": {"name": {"en": "English name for your Product","de": "German name for your Product"},"categories": [],"categoryOrderHints": {},"slug": {"en": "human-readable-url-for-english-product","de": "human-readable-url-for-german-product"},"masterVariant": {"id": 1,"prices": [],"images": [],"attributes": [],"assets": []},"variants": [],"searchKeywords": {}},"published": false,"hasStagedChanges": false},"key": "new-product-key","lastVariantId": 1}
Return a Product by its Key
Your new Product key can be queried by adding .withKey({ID: {productKey}}) after the .products() endpoint:
const returnProductByKey = (productKey: string) => {return apiRoot.products().withKey({ key: productKey }).get().execute();};returnProductByKey('new-product-key').then(({ body }) => {console.log(JSON.stringify(body));}).catch(console.error);
When this code is run, you retrieve all the data of the Product.
If no Product exists with your specified key, the API returns a 404 Not Found error.
Using the TypeScript SDK in the browser
The TypeScript SDK can also be used in a web browser.
Create an HTML file and insert the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><title>TypeScript SDK Examples</title><script src="https://unpkg.com/@commercetools/sdk-client-v2@0.2.0/dist/commercetools-sdk-client-v2.umd.js"></script><script src="https://unpkg.com/@commercetools/platform-sdk@1.20.0/dist/commercetools-platform-sdk.umd.js"></script></head><body><!-- Click this button to return the Project details --><p><button onclick="getProjectDetails()">Get Project Information</button></p><!-- This text is overwritten when getProjectDetails() finishes --><p id="details">Click the above button to display the Project information.</p></body><script>// Enter your API client configurationvar oauthUri = 'https://auth.{region}.commercetools.com';var baseUri = 'https://api.{region}.commercetools.com';var credentials = {clientId: '{clientID}',clientSecret: '{clientSecret}',};var projectKey = '{projectKey}';// Builds the clientvar { ClientBuilder } = window['@commercetools/sdk-client-v2'];var client = new ClientBuilder().defaultClient(baseUri, credentials, oauthUri, projectKey).build();var { createApiBuilderFromCtpClient } =window['@commercetools/platform-sdk'];var apiRoot = createApiBuilderFromCtpClient(client).withProjectKey({projectKey,});// Returns the Project detailsfunction getProjectDetails() {apiRoot.get().execute().then(function ({ body }) {window.document.getElementById('details').innerHTML =JSON.stringify(body);});}</script></html>
When loaded in your web browser this page displays a button that, when clicked, returns your Project information.
The getProjectDetails() function is similar to previous code examples within this getting started guide. Consult the previous code examples to add further functionality to the HTML document.